Introduction
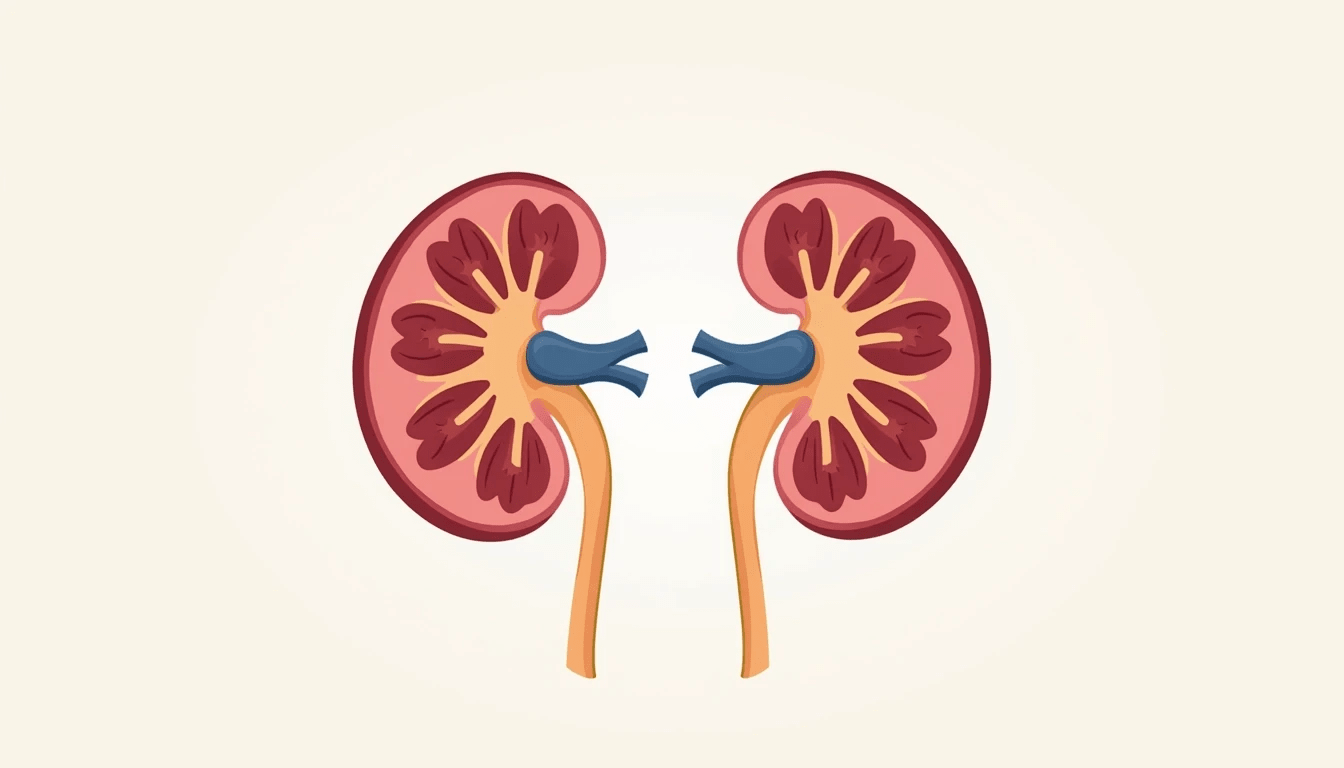
The kidney labeled model is an in-depth human kidney diagram which illustrates its anatomy and important functionalities. Based on this model, medical students, researchers and educators can better understand the structure of the kidney and its function in filtration and waste disposal. A kidney is a vital organ that balances fluids in the body and removes toxins. Kidney Diagram – Each part tells a story, and when visually represented through a diagram one can make sense out of an otherwise memory-intensive explanation.
Significance of Kidney Imaged Model Image Guide
A detailed labeled diagram/template of the kidney that comes used as an educational purpose as it tends to provide an accurate representation of the internal and external structures of kidney. These anatomies help to visualize the renal cortex, medulla, pelvis, nephrons, etc. An accurate diagram of the kidneys eases the understanding of intricate anatomy in different settings including classrooms as well as medical exploration.
Tissue Organization of the Kidney External Structure of the Kidney
External Structure of the Kidney:
- Renal Capsule: The fibrous outer coat of the kidney.
- Hydronephrosis: A condition where urine over dilates the kidneys.
- Cortex and Medulla — the outer and inner areas responsible for maintaining key filtration functions
Knowledge about these external characteristics serves the purpose in disease diagnosis and medical research of kidney.
The Microscopic Anatomy of the Kidney
Containing Internal Structure Responsible For The Formation Of The Urine Key parts include:
Renal Cortex: The outer part of the kidney, which contains the nephrons where the filtration process starts.
Renal Medulla – Contains renal pyramids that allow for urine concentration.
Renal Pelvis: Where urine collects before going into the ureter.
Each type of component is essential to sustaining homeostasis and filtering blood efficiently.
Nephron — the kidney functional unit
Blood filtering units in the kidneys are called nephron, and it is the fundamental unit of the kidney. It consists of:
- Glomerulus: kidney structure found in nephron, filter blood.
- Bowman’s Capsule: Encase the glomerulus and accumulate the filtrate.
- Loop of Henle: Balances blood water and salt.
- Collecting Ducts: Move urine to the renal pelvis
Knowledge of nephron function is key to understanding kidney disease and treatment.
Blood Supply to the Kidney
Blood enters the kidney via the renal artery and is filtered through a network of capillaries. The renal vein returns filtered blood to circulation. Key points include:
Afferent Arterioles: Deliver blood to the glomerulus.
- Transport filtered blood away (Efferent Arterioles)
- Peritubular Capillaries: Reabsorb needed molecules and water.
A steady flow of blood keeps the kidney working, which in turn protects the body from toxin buildups.
DESCRIBE KIDNEY FUNCTION AND FILTRATION PROCESS
Kidney carries out several important functions:
Filtration: This is the process of removing poisons, excess salts, and waste.
Reabsorption: Absorbs back needed nutrients and water.
Secretion: Removes extra waste in the form of urine.
Urination: Excretes urine through the ureter into the bladder
These functions balance electrolytes, regulate blood pressure, and promote overall health.
Common Kidney Diseases and How To Diagnosis
Diseases related to kidneys can deeply affect health as a whole. A few of these typical conditions are:
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Slow reduction in kidney functioning.
Kidney Stones: Hard deposits that block urine flow
Bacterial Kidney Infections: Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Kidney Failure: Total loss of kidney function.
Blood tests, urine analysis, imaging scans, and biopsies are used to help doctors identify the underlying issue, and address any problems with the kidneys.
FAQs
What is a kidney labeled model used for?
The kidney structures are very well visible and can help people to understand function of the kidney and filtration process in visual and detail way.
Which are the lobes in a diagram of the organ: kidney?
Components of the kidney: renal cortex, medulla, pelvis, nephrons, renal blood vessels.
How does the kidney clean blood?
Blood flows into the glomerulus, the network of blood vessels that filters waste and excess fluids, while reabsorbing key nutrients before those wastes and excess fluids are excreted as urine.
Common kidney disease and Kidney diseases
Chronic kidney disease, kidney stones, urinary tract infections, kidney failure are some of the common kidney ailments.
Importance of studying the kidney as a labeled model.
It assists medical students, educators, and researchers in visualizing kidney anatomy, which can aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.